
What is Last Mile? A Complete Guide to Last Mile Delivery & Logistics
Learn about the last mile, last mile delivery, and last mile logistics. Discover how this crucial phase impacts supply chains, customer satisfaction, and delivery efficiency.
By Komal Puri | October 10, 2022
Consumer buying behaviors have evolved significantly, particularly in the realm of online shopping.
Modern consumers now demand cheap—or even better, free—and fast delivery.
Let's emphasize that: free, fast delivery.
To remain competitive, companies must improve efficiency and reduce costs within their shipping logistics.
A crucial focus area is optimizing the last mile delivery process. For a company to thrive in today's market, streamlining efficiency in this crucial stage is essential.
This article delves deeply into the intricacies of last mile delivery logistics, identifies key challenges of last mile deliveries expected in the future, and explores how leveraging technology can effectively mitigate these challenges, thereby providing your company with a competitive edge.


Here’s a table of contents:
- What is Last Mile?
- Why the last mile is critical in supply chains
- The Evolution of Last Mile
- The Concept of Last Mile in Logistics
- What is Last Mile Delivery?
- What is the “Last Mile Delivery Problem”?
- 6 Ways Technology Can Solve Your Biggest Challenges
- 7 Trends That Will Continue to Shape (and Change) Last Mile Delivery in 2024

What is Last Mile?
The term "last mile" refers to the final step in a broader process of delivery, service provision, or connectivity that brings products or services directly to end users. It’s often the most critical and complex stage, where a company or service must efficiently bridge the gap between a central hub or provider and the customer's location, whether it’s a home, office, or other destination.
Why the last mile is critical in supply chains
The last mile is critical in supply chains because it directly impacts customer satisfaction, costs, and operational efficiency. It’s often the most expensive part of the delivery process due to factors like traffic, multiple stops, and failed deliveries. A smooth last mile ensures timely and accurate deliveries, which boosts customer loyalty. It also serves as a key differentiator for businesses in competitive markets. Lastly, optimizing the last mile can address sustainability concerns, as it’s where most emissions and inefficiencies occur. Efficient last mile operations are crucial for both customer retention and profitability.
The Evolution of Last Mile
The last mile concept has evolved significantly over time, driven by advancements in technology, urbanization, and changing consumer expectations. Here’s a look at its historical development:
- Early Postal Services:
- Last mile originated with postal workers delivering mail and parcels, often on foot or by bike.
- Retail and Parcel Delivery:
- Home delivery services for newspapers, groceries, and other goods became common in the mid-20th century.
- E-Commerce Boom:
- The rise of Amazon and eBay in the late 1990s transformed the last mile, emphasizing speed and delivery accuracy for individual parcels.
- Technological Advancements:
- The 2010s introduced GPS tracking, AI-driven route optimization, and real-time updates, enabling faster and more efficient last mile deliveries.
- Sustainability and Hyperlocal Delivery:
- Focus on green delivery methods (EVs, bikes) and hyperlocal models (1-hour deliveries) emerged to meet consumer and environmental demands.
- Future Trends:
- Automation through drones, autonomous vehicles, and robots will further optimize last mile efficiency.


The Concept of Last Mile in Logistics
1. Origin of the Term: Where and How It Was First Used
- The term “last mile” originated in the telecommunications industry in the early 20th century, referring to the final leg of delivering telephone or internet services from the provider to a customer's home or business.
- Over time, it was adopted by the logistics industry to describe the final step in delivering goods from a transportation hub to the end customer.
2. Last Mile vs. Long-Haul Transportation: Key Differences
- Long-haul transportation involves moving goods over long distances, often across cities or countries, usually in bulk on large trucks, ships, or planes.
- The last mile focuses on short-distance, individual deliveries directly to the customer’s location. It involves multiple stops and often encounters urban traffic and accessibility challenges, making it more complex and costly.
3. The Role of Last Mile in Connecting the Supply Chain to the End Customer
- The last mile is the final connection between the supply chain and the customer. It completes the delivery journey and determines whether the product reaches the customer as expected.
- As the most visible part of the logistics process, it plays a key role in customer satisfaction, influencing the overall experience and brand perception.
4. Importance of Speed and Accuracy in the Last Mile Phase
- Speed and accuracy are crucial in the last mile phase because consumers now expect fast deliveries, with same-day or next-day services becoming the norm.
- Mistakes or delays in this stage, such as incorrect addresses or missed delivery windows, can lead to customer dissatisfaction and increase operational costs due to re-deliveries or returns.
What is Last Mile Delivery?
Last mile delivery is the final leg of the e-commerce supply chain that physically connects brands with consumers through the delivery of the purchase. Goods are transported from a warehouse or a distribution center and arrive either at a consumer’s home, business, or parcel locker. For the shipper, last-mile delivery is the most complex and expensive part of the product’s journey.
The goal of superior last- mile delivery is to enable every delivery to reach its destination every time, on time, accurately, efficiently, and sustainably.
This step is crucial in the delivery process, and businesses strive to make it as fast and efficient as possible to meet the growing consumer demand for rapid shipping, particularly in sectors like e-commerce, food, and retail industries. It's also the most costly part of the journey for goods to reach their final destination.


5 Key Steps in the Last Mile Delivery Process
The last mile delivery process can be divided into five main steps:
Step #1:
Orders are entered into a centralized system
In this initial step, orders and requests are tracked both by the sender and the recipient, who likely monitors the status of their delivery through a tracking number.
Step #2:
Orders arrive at the transportation hub and await delivery
Here is where the last mile delivery phase officially begins. The goal is to move the order from the transportation hub to the customer as quickly as possible.
Step #3:
Orders are assigned to delivery personnel based on routes and addresses
Strategically sorting and assigning parcels for delivery is key to optimizing last mile logistics for a cost-effective and efficient solution.
Step #4:
Orders are scanned before being loaded onto delivery vehicles
Scanning updates the order status for both the sender and the recipient, minimizing the risk of packages being lost during transit.
Step #5
Orders successfully reach their final recipients, and proof of delivery is obtained.
At this point, the package has arrived at its intended destination. The delivery personnel then updates the tracking information to verify and confirm that the delivery has been completed.
What is the “Last Mile Problem”?
We’ve already established that having an efficient last mile delivery process is crucial for keeping customers satisfied.
However, here’s the paradox: while customers expect fast and free shipping, the last mile is actually the most expensive and time-consuming part of the entire shipping process.
With consumers easily finding alternative places to shop, companies cannot afford to let them down. This means companies often absorb these costs.
And that’s the essence of the last mile delivery problem.
Last mile shipping can account for up to 53% of the total cost of a shipment. While companies typically cover around 25% of these costs, this figure is rising due to increasing inefficiencies within the supply chain.
What’s the biggest challenge with last mile deliveries?
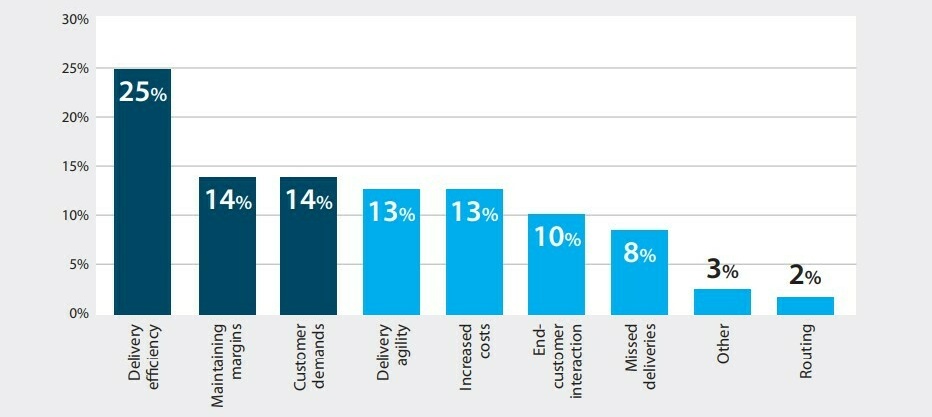
Graph showing last mile delivery challenges Source
What are the challenges in last mile logistics?
Last mile delivery is a complex process that involves several challenges that can impact delivery times, costs, and customer satisfaction. Here are ten common challenges:
- Traffic Congestion: Traffic congestion can significantly impact delivery times, making it difficult for drivers to reach customers on time.
- Limited Visibility: Last mile delivery can be challenging to manage because it is difficult to track packages once they are out for delivery, leading to limited visibility for both logistics companies and customers.
- Missed Deliveries: Undelivered packages pose a significant issue in the final stages of the delivery process, resulting in extra expenses for logistics firms and dissatisfaction among customers.
- Managing Returns: Returns management is a complex process in that happens in last stage, requiring significant resources and logistics coordination to ensure that packages are returned to the appropriate location and processed in a timely manner.
- Delivery Window Constraints: Customers often have specific delivery windows that can be challenging to meet, leading to missed deliveries and reduced customer satisfaction.
- Cost Management: The final leg of the delivery process can be costly, particularly in urban areas where traffic and other challenges can increase delivery times and costs.
- Unpredictable Demand: Managing this last leg can prove difficult due to unpredictable demand patterns, leading to inefficient use of resources and additional costs.
- Security and Theft: Packages in the final mile stage are vulnerable to theft and damage, which can result in significant financial losses for logistics companies and frustration for customers.
- Environmental Impact: The environmental impact caused in this stage is significant due to emissions from delivery vehicles and packaging waste.
- Limited Access: In remote and rural regions, where access to roads and infrastructure is limited, the delivery process becomes even more challenging, leading to extended delivery times and increased expenses.
Optimizing last mile delivery can lead to significant cost savings for ecommerce businesses and retailers, especially as shipment volumes continue to surge across industries.
In the next section, we’ll explore best practices for improving your last mile logistics.


5 Ways How Technology Can Solve the Biggest Last Mile Delivery Challenges
Perfecting last mile delivery to ensure fast, on-time deliveries is crucial for delivering a great customer experience. But how can you achieve that perfect last mile delivery?
A good place to start is by using an effective fleet management tool.
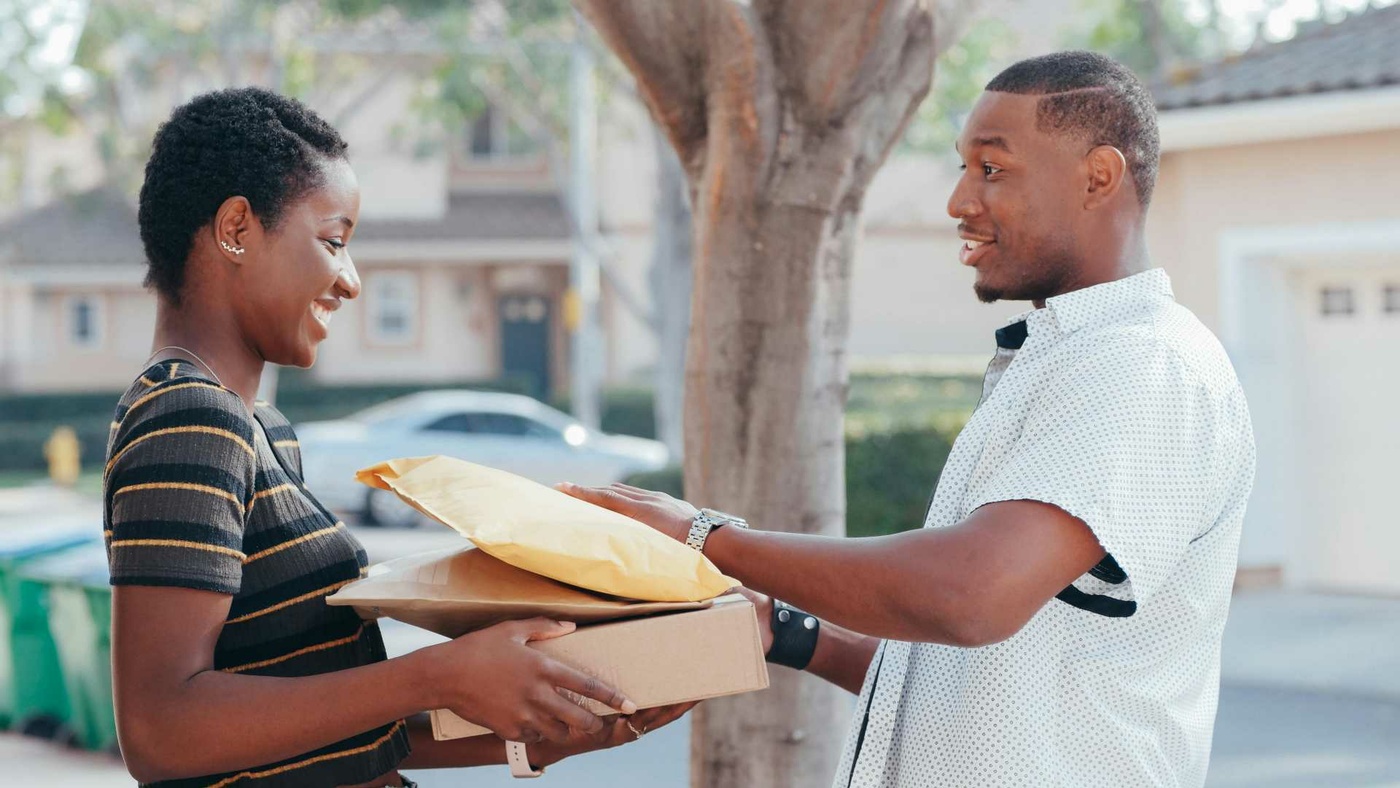
FarEye is a last mile delivery platform designed to help you master this critical last mile part of the delivery process. Trusted by companies like GAP, Total Wine & More, MedMen, Imperfect Foods, and United Supermarkets, FarEye provides a "complete toolkit for last mile delivery." It includes features such as end-to-end route planning, dispatching, real-time driver tracking, communication, and analytics.
In other words, the technology handles the heavy lifting, allowing you to focus on your customers.
Here are five ways a last mile delivery solution like FarEye can help streamline your delivery process:
1. Use route planning to reduce delivery times
Every driver follows a route for deliveries. Ideally, these routes are simple, with multiple drop-offs along the way.
In reality, routes can span many miles with just a few deliveries, especially in rural areas, which means wasted time and fuel for fewer deliveries.
In urban areas, heavy traffic can eat up just as much time and fuel, despite shorter distances between drop-offs.
FarEye optimizes delivery routes by considering factors like time, location, vehicle capacity, and traffic to recommend the most efficient routes. Any real-time traffic updates are sent to drivers via SMS, keeping them on the best route and informing customers in real-time.

2. Reduce service time and labor costs with auto dispatching
In addition to optimizing routes, using software to plan deliveries saves the time needed for manual planning. Since routes update in real-time, fewer drivers are needed to complete deliveries in a day.
Managers can create auto-assignment rules based on driver location, route distance, and task limits per driver.

This dispatch feature introduces a new level of automation, helping to save time, optimize resource allocation, and allowing managers to focus on improving other aspects of the delivery process. By streamlining last mile logistics, it also helps to reduce inefficiencies that often lead to higher delivery costs.
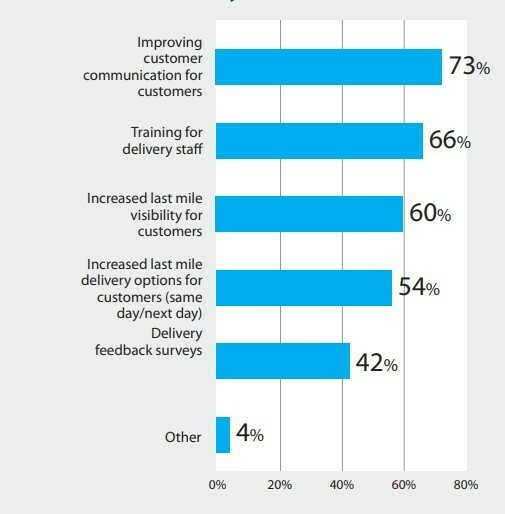
In fact, an industry study revealed that 56% of consumers are demanding greater transparency in the delivery process.
But what other features are customers expecting from their last mile services?
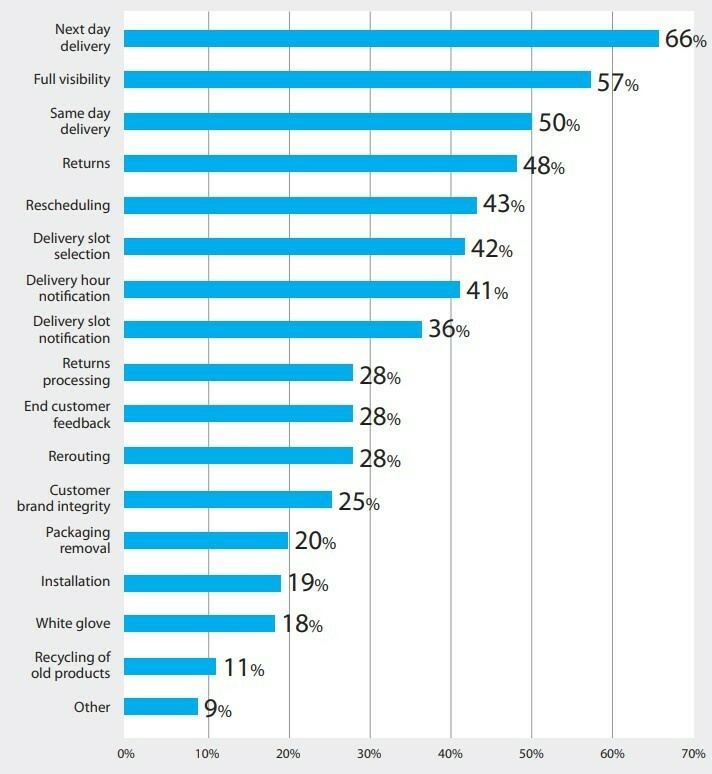
One key expectation is proof of delivery. This involves verifying that an item has been successfully delivered, whether through a recipient’s signature or a photo of the package at the doorstep, complete with a time and date stamp.
FarEye makes proof of delivery simple. Drivers can capture signatures, take photos, scan barcodes, or add notes using a mobile app. This ensures both the sender and the recipient have confirmation that the delivery was successful.

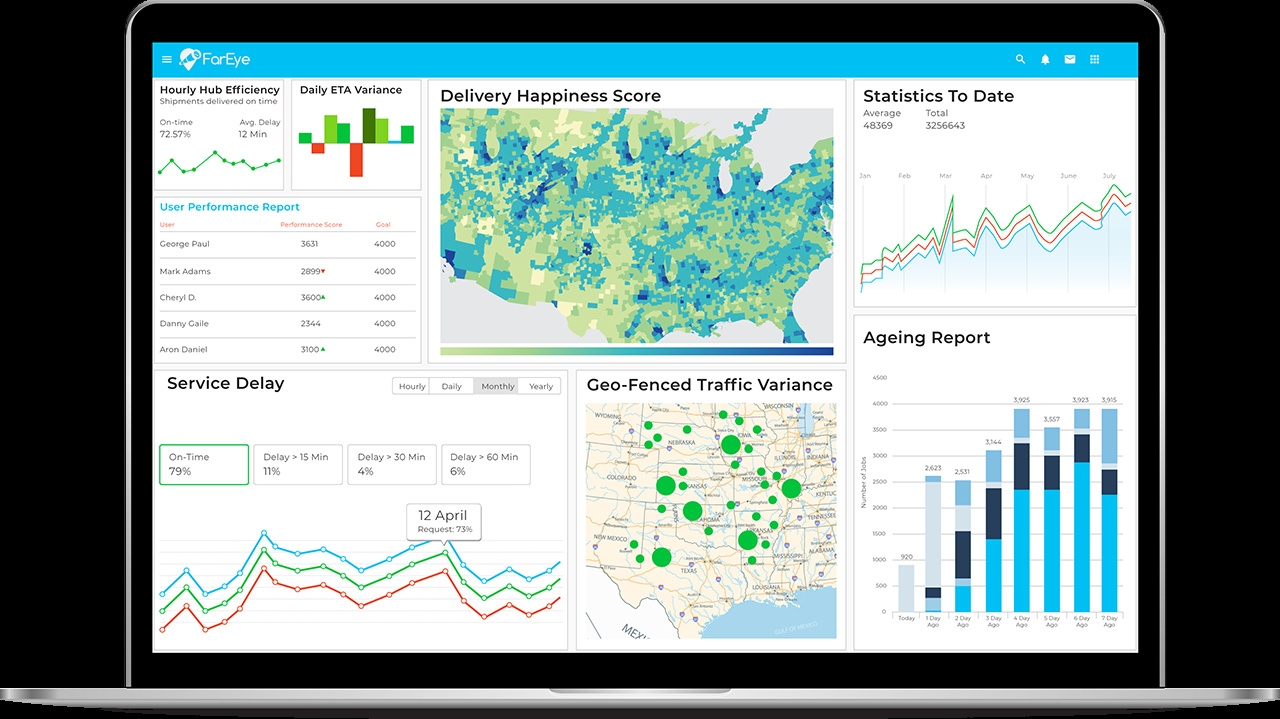
4. Use reporting to increase accountability
Reporting helps identify bottlenecks before they escalate into bigger issues and highlights areas for improvement.
FarEye’s platform tracks key metrics such as success rates, on-time performance, service times, feedback scores, and distance traveled. This data can be filtered by team, driver, or time period, and you can export it to generate custom reports.
By tracking these KPIs, you gain insight into your last mile supply chain and can better understand how time and resources are being used.
5. Enhance the customer experience
Improving customer communication involves more than just providing a tracking number. Consumers now expect more from delivery services.
With FarEye, customers can do more than track their orders—they can communicate directly with the driver, receive SMS notifications about their delivery, and engage in a real-time feedback loop.
7 Trends That Will Continue to Shape (and Change) Last Mile Delivery in 2025
Companies are continuously testing and implementing new strategies to perfect the last mile delivery process and keep pace with evolving consumer expectations. Here are seven trends:
1. Rapid order fulfillment
More consumers now expect on-demand or same-day delivery, putting increasing pressure on logistics and fulfillment processes.
Businesses are required to turn orders around quickly—often faster than existing technology can handle.
“What would typically take less than an hour suddenly needs to be done within minutes, which creates planning challenges,” says Michael Armanious, vice president of sales and marketing at Datexcorp, a third-party logistics (3PL) company, in an article from Supply Chain Dive.


2. Improved traceability
Traditional last mile delivery carriers have made significant improvements in package traceability, incorporating features such as real-time tracking and proof of delivery.
These updates play a crucial role in ensuring packages don’t get lost, or locating them when they do. Advanced smartphone apps have transformed the way packages are tracked. For instance, solutions like FarEye offer GPS functionality that allows recipients to monitor their package on a map and track the driver’s exact location.
Proof of delivery options—such as signatures, time stamps, and details about where the package was left—help minimize disputes between carriers and customers, improving the overall last mile delivery experience for both parties.
3. In-house delivery services
More companies, including e-commerce giant Amazon, are using their own in-house delivery services.
In-house delivery gives businesses control over their own fleet of vehicles and employs salaried drivers to handle shipments directly from warehouses to customers. This control allows companies to manage costs, improve the customer experience, and extend delivery windows to include evenings and weekends.
4. Micro warehousing
Amazon continues to lead the way with its micro warehousing strategy, operating over 58 transportation hubs across the U.S. that support same-day delivery via Prime Now.
This trend has prompted other organizations to allocate or purchase additional warehouse space to enable faster deliveries.
While many retailers have successfully reduced delivery times to two days, Amazon still sets the standard, delivering parcels in as little as two hours. Competitors have considerable ground to cover.
5. Carrier upsells
E-commerce companies have long used data to suggest additional products to customers based on their browsing and purchase history. Now, this upsell strategy is being adopted by last mile delivery carriers, with some experimenting with product upsells at the point of delivery.
For instance, if a customer regularly orders oral hygiene products each month, the delivery driver could offer a tube of toothpaste along with the order. Similarly, if a customer has purchased gardening supplies, the driver might suggest grass seeds or fertilizer as an additional purchase.
6. Smart technology
The range of products ordered online is expanding rapidly, with consumers now purchasing perishable goods like fresh food, frozen items, and even live products like plants and pet fish. These items require special shipping conditions to preserve their quality.
Fulfillment centers are adopting smart technology to manage these shipments, using tools to control temperature, humidity, and air quality. Additionally, route planning now takes into account factors like weather conditions, and extra packing materials are often necessary to protect temperature-sensitive shipments.


7. Robots and drones
While not yet mainstream, robots and drones are set to revolutionize last mile delivery in the near future.
Andre Pharand, Accenture’s global management consulting lead for the postal and parcel industry, explains in a Supply Chain Dive article: “If parcels can be delivered by autonomous vehicles or drones, that will drastically alter the landscape. Labor costs represent 60% of delivery expenses. Automating delivery with robots and drones would eliminate those constraints and allow deliveries to be completed 24 hours a day.”
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, we’ve explored what last mile delivery entails, the associated challenges and costs, ways to optimize your last mile delivery process, and emerging trends to keep an eye on in the future.
If you’re ready to take your last mile delivery operations to the next level, reach out to our sales team or schedule a demo today.
Sustainability and Green Logistics in Last Mile Delivery
Sustainability in last mile delivery is becoming increasingly critical as e-commerce continues to expand, driving up carbon emissions. Businesses are focusing on eco-friendly practices to minimize their carbon footprints, particularly through the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). Transitioning to EVs significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional delivery vans, which heavily add to urban pollution due to their stopping and starting. Several industry giants are investing in electric fleets, setting a precedent for sustainable operations that align with consumer demand for greener solutions.
Another effective strategy is route optimization, which employs advanced algorithms to determine the most efficient delivery paths. This not only reduces fuel consumption but also enhances delivery success rates by minimizing missed deliveries and unnecessary trips. Additionally, businesses are re-evaluating their packaging methods to ensure they are using efficient and sustainable materials. By reducing excess packaging and utilizing recyclable materials, businesses can further decrease their environmental impact while appealing to the growing economically conscious consumers. These combined efforts not only help in achieving corporate sustainability goals but also help build a brand image in the market.
Customer Experience in Last Mile Delivery
Last mile delivery is a critical component of the supply chain that significantly influences customer satisfaction, retention, and brand loyalty. As the final stage of the delivery process, it is where customers directly interact with the brand, making it essential for businesses to enhance this experience. Research indicates that timely and reliable deliveries are paramount; customers expect their orders to arrive within their preferred timeframes. Businesses that effectively manage logistics and utilize technologies such as real-time tracking and route optimization can enhance delivery reliability, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Personalized delivery experiences are increasingly vital in today’s competitive market. Offering flexible delivery options such as same-day or next-day service and allowing customers to select their preferred delivery windows can significantly enhance their overall experience. Additionally, real-time communication throughout the delivery process, including updates on estimated arrival times and proactive notifications about delays, helps to manage customer expectations and reduce anxiety. This level of transparency builds trust and encourages repeat business. By integrating these strategies into their operations, businesses can not only meet but exceed customer expectations, ultimately leading to higher retention rates and stronger brand loyalty.
How Last Mile Delivery Automation Reduces Costs and Errors
Automation in last mile delivery significantly enhances operational efficiency and reduces costs through the implementation of advanced software tools such as route planning and predictive analytics. Route planning software utilizes algorithms that analyze various factors, including traffic patterns, delivery windows, and vehicle capacity, to determine the most efficient delivery routes. This optimization minimizes travel distances and time, leading to reduced fuel consumption and lower operational costs. Businesses that adopt these technologies can decrease delivery times and enhance on-time delivery rates, which directly impacts customer satisfaction and retention.
Predictive analytics further complements route optimization by leveraging historical data and real-time information to forecast demand and identify potential delivery challenges. By predicting the likelihood of successful deliveries based on variables like weather conditions, time of day, and customer behavior, businesses can proactively adjust their delivery schedules and resource allocation. This capability not only reduces missed deliveries which are often a significant source of operational inefficiency but also allows businesses to allocate their resources more effectively, ensuring that drivers are utilized optimally. As a result, businesses that integrate these automated solutions can achieve substantial reductions in delivery errors and operational costs while improving overall service quality.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the steps in the last mile delivery process?
The last mile delivery process typically involves the following key steps:
1. Order Received: Orders are entered into a centralized system for tracking.
2. Arrival at Distribution Center: Packages arrive at a hub where they await dispatch.
3. Allocation to Delivery Personnel: Orders are assigned to delivery drivers based on routes and addresses.
4. Preloading and Scanning: Packages are scanned before being loaded onto delivery vehicles to update their status.
5. Final Delivery: The package is delivered to the recipient.
Is last mile delivery profitable?
Last mile delivery can be challenging to profit from due to high operational costs, which account for over 40% of total shipping expenses. Many businesses struggle to cover these costs, often leading to reduced profit margins. However, businesses that optimize their last mile processes can improve profitability by enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Why is last mile delivery so expensive?
Last mile delivery is expensive primarily due to logistical challenges such as:
- Complexity of Routes: Delivering to multiple unique destinations increases time and fuel costs.
- High Operational Costs: It often requires maintaining a larger fleet and more drivers for smaller packages.
- Consumer Expectations: The demand for faster delivery options, such as same-day service, adds pressure on logistics providers.
Who needs last mile delivery?
Last mile delivery is essential for various sectors, including:
- E-commerce
- Food Delivery
- Retail
- Healthcare Providers
- Pharmaceuticals
- Logistics Companies
How long does last mile delivery take?
The duration of last mile delivery can vary significantly based on factors such as location, traffic conditions, and the efficiency of the logistics provider. Generally, it can range from a few hours for local deliveries to several days for more remote areas. Many businesses aim for same-day or next-day delivery to meet consumer expectations.

Komal Puri is a seasoned professional in the logistics and supply chain industry. As the AVP of Marketing and a subject matter expert at FarEye, she has been instrumental in shaping the industry narrative for the past decade. Her expertise and insights have earned her numerous awards and recognition. Komal’s writings reflect her deep understanding of the industry, offering valuable insights and thought leadership.