- Sustainability
Assessing EV Readiness: Your Essential Checklist for Sustainable Logistics
The logistics industry is experiencing significant transformations as global priorities shift toward sustainability, with electric vehicles (EVs) emerging as a crucial solution to balance operational efficiency and environmental responsibility. The European Environment Agency warns that logistics could account for up to 40% of global carbon dioxide emissions by 2050 if effective measures are not implemented. In 2023, the green logistics market was valued at approximately USD 1.16 trillion, with projections indicating a CAGR of over 9.5% from 2024 to 2032. This growth is driven by stringent environmental regulations, increasing carbon pricing, and heightened consumer demand for sustainable practices.
Notably, logistics plays a critical role in corporate sustainability, as 70-90% of a business's carbon footprint often comes from Scope 3 emissions, which include supply chain activities. Companies like One of the World's largest Furniture Retailer, Amazon, DHL, and Maersk are spearheading the adoption of eco-friendly practices, leveraging electric vehicles, optimized routing, and renewable energy solutions to align with regulatory standards and meet evolving consumer expectations. These efforts are essential as global consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability; one in ten people rank “environmentally friendly” and “sustainability” as key attributes influencing their brand choices.
Financial pressures further underscore the urgency of adopting sustainable practices, with carbon prices projected to reach $50-$100 per ton by 2030, creating significant risks for non-compliant logistics providers. For organizations, the path forward demands an actionable strategy. This includes assessing EV readiness, integrating sustainable technologies, and fostering collaboration with supply chain partners to reduce carbon emissions. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed roadmap for businesses to adopt sustainable logistics and position themselves as leaders in a rapidly evolving industry.
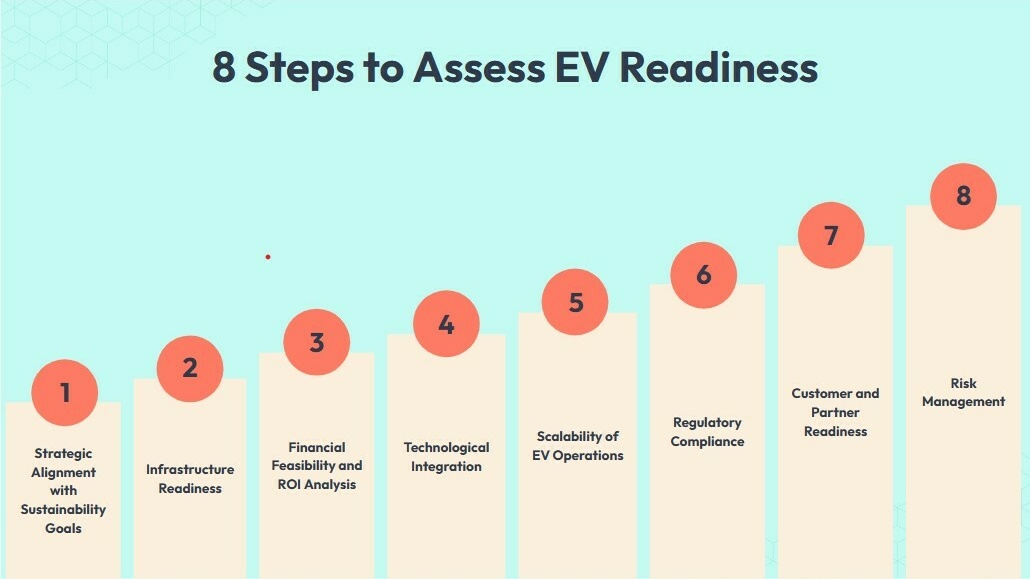
1. Strategic Alignment with Sustainability Goals
Aligning electric vehicle adoption with broader sustainability objectives is essential for organizations. Here’s how:
Defining Goals: Companies like One of the World's largest Furniture Retailer and Amazon exemplify how setting ambitious targets, such as One of the World's largest Furniture Retailer's goal of 100% zero-emission deliveries by 2025 can drive the integration of EVs into sustainability strategies.
Global Initiatives: The urgency of decarbonizing logistics is underscored by agreements like the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global warming. The World Economic Forum estimates that achieving net-zero supply chains could significantly reduce global emissions.
Stakeholder Buy-in: Engaging both internal and external stakeholders is crucial for success. Walmart’s Project Gigaton aims to cut 1 billion metric tons of greenhouse gasses from its supply chain by 2030. It highlights the importance of collaboration with suppliers and partners.
2. Infrastructure Readiness
A robust infrastructure is vital for facilitating EV operations and ensuring scalability. Key components include:
Charging Infrastructure: The availability of charging stations is critical. UPS's investment in urban micro hubs highlights the importance of accessible charging solutions for last-mile deliveries.
Renewable Energy Integration: Companies like DHL and One of the World's largest Furniture Retailer are successfully powering their EV fleets with renewable energy, aligning with sustainable energy principles and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Geographic Considerations: Infrastructure readiness varies globally, with Europe leading in EV ecosystem development due to supportive government policies, while emerging markets are enhancing accessibility through public-private partnerships.
3. Financial Feasibility and ROI Analysis
Understanding the financial implications of EV adoption is crucial for organizations. This involves:
Initial Costs and Incentives: Although EVs typically have higher upfront costs, government incentives can help reduce these expenses significantly. For instance, the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act offers tax credits that encourage EV purchases.
Operational Savings: Studies indicate that EVs can reduce the total cost of ownership by approximately 20% compared to traditional diesel vehicles, primarily due to lower fuel and maintenance costs.
Long-term ROI: McKinsey research suggests that companies investing in EVs can realize a return on investment within five years, driven by operational savings and increased customer loyalty to sustainable practices.
4. Technological Integration
Leveraging advanced technologies is essential for optimizing EV performance and ensuring operational efficiency. Important technologies include:
Route Optimization Software: AI-powered electric vehicle routing solutions help minimize energy consumption during deliveries. FedEx's use of such technology exemplifies how logistics can maximize the range of their EVs.
Telematics and Monitoring: Real-time data management through telematics allows companies like Walmart to monitor battery health, energy consumption, and fleet performance, ensuring smooth operations.
Condition-Based Monitoring: Implementing condition-based monitoring allows organizations to track the health of critical vehicle components. This technology ensures that issues are identified early, reducing the risk of unexpected failures and improving fleet uptime.
5. Scalability of EV Operations
To successfully scale EV adoption, organizations should consider a phased approach:
Phased Deployment: Initiating pilot projects allows companies to test EV integration in controlled environments before expanding. FedEx and One of the World's largest Furniture Retailer have both adopted this strategy. One of the World's largest Furniture Retailer started its EV rollout in high-density cities like Shanghai and London, where infrastructure was more accessible.
Battery Lifecycle Management: Sustainable practices in battery recycling are crucial. DHL collaborates with Umicore, a circular technology company, to ensure that used EV batteries are recycled responsibly.
Global Adoption Trends: The IEA Global EV Outlook 2023 reports a significant increase in EV sales within logistics fleets. This indicates a growing trend towards electrification across the industry.
6. Regulatory Compliance
Staying compliant with sustainability compliances is essential for avoiding penalties and enhancing sustainability credentials:
Government Policies: The European Union’s Green Deal requires all new vehicles to be zero-emission by 2035. This has prompted companies like One of the World's largest Furniture Retailer and Maersk to accelerate EV adoption. In India, the FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles) scheme supports the electrification of commercial fleets through subsidies and grants.
Sustainability Reporting: Transparency in reporting sustainability metrics is vital for accountability. Amazon’s detailed annual reports on carbon reductions achieved through its EV initiatives exemplify this commitment.
Compliance Benefits and Consequences: Compliance with regulations helps avoid significant penalties while offering substantial rewards. Companies following the EPA Clean Trucks Plan can save billions in fuel and maintenance costs and enhance their brand reputation. Non-compliance can lead to severe financial repercussions and hefty fines.
Emission Standards: Meeting stringent emission caps is necessary for compliance. Walmart’s fleet electrification efforts align with California’s Advanced Clean Trucks regulation, showcasing proactive measures taken by businesses.
7. Customer and Partner Readiness
Engaging customers and partners effectively ensures that the transition to EVs aligns with stakeholder expectations:
Eco-Conscious Consumer Demand: A significant portion of consumers are willing to pay more for sustainable delivery options, as evidenced by Deloitte's findings. Companies like Etsy cater to this demand through carbon-neutral shipping practices.
Partner Collaboration: Working with suppliers and logistics partners ensures seamless EV integration. For example, Unilever collaborates with logistics providers to electrify its supply chain, reducing emissions across the value chain.
Brand Value Enhancement: Prioritizing sustainability not only improves environmental footprints but also strengthens brand reputation. DHL’s GoGreen initiative serves as a model for enhancing brand value through sustainable practices.
8. Risk Management
Identifying potential risks associated with the transition to EVs is critical for ensuring a smooth implementation process:
Addressing Power Outages: Organizations must prepare for potential power disruptions by installing backup systems. Amazon’s use of auxiliary power units at depots exemplifies proactive risk management strategies.
Battery Supply Chain Challenges: Securing sustainable sources for battery materials is essential. Partnerships with ethical mining companies help firms like Maersk mitigate risks related to battery supply chains.
Future-Proofing Logistics: Exploring alternative technologies, such as hydrogen-powered trucks being researched by Daimler and Volvo, ensures flexibility in adapting to future logistics needs.
Conclusion
The transition to electric vehicles within the logistics sector is not just a strategic choice but a necessity in the face of escalating environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. As the logistics industry grapples with the potential to contribute significantly to global carbon emissions, organizations must prioritize sustainability by aligning EV adoption with their broader business goals. This involves assessing infrastructure readiness, evaluating financial feasibility, and integrating advanced technologies to optimize operations. Companies like One of the World's largest Furniture Retailer, Amazon, and DHL are leading the charge by implementing innovative solutions that not only enhance operational efficiency but also resonate with an increasingly eco-conscious consumer base. Ultimately, the successful integration of EVs into logistics operations hinges on a comprehensive roadmap that includes stakeholder engagement, compliance with regulations, and a commitment to continuous improvement in sustainability practices. By adopting these changes, organizations can position themselves as leaders in a rapidly evolving market while contributing positively to global sustainability efforts.

Komal Puri is a seasoned professional in the logistics and supply chain industry. As the AVP of Marketing and a subject matter expert at FarEye, she has been instrumental in shaping the industry narrative for the past decade. Her expertise and insights have earned her numerous awards and recognition. Komal’s writings reflect her deep understanding of the industry, offering valuable insights and thought leadership.
Let's Talk to Our Experts and Optimize Your Deliveries Today!
An expert from our team will reach out within 24 hours
Related resources



